UWB
What is the difference between UWB and Bluetooth?
| Type | UWB | Bluetooth |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Band | GHz range | 2400 ~ 2483 MHz |
| Communication Range | 100m | 10m |
| Transfer Rate | 1~100Mbps | 1Mbps |
| Power Output | 0.2~2mW | 1mW |
UWB can achieve higher accuracy and broader applicability than Bluetooth due to its use of a much wider frequency band.
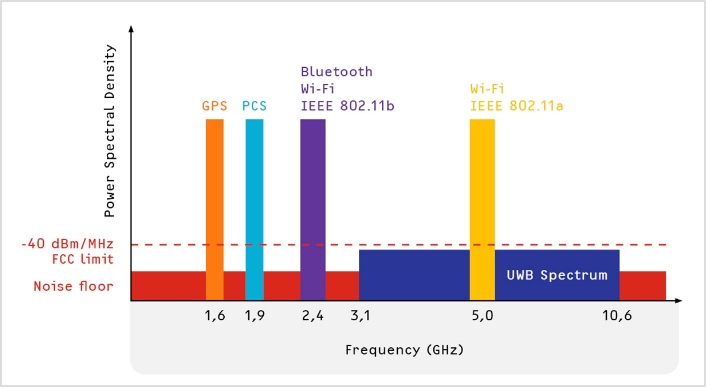

[Comparison of Narrowband, Wideband, CDMA, and UWB Spectrums]
As shown in the figure above, when comparing three systems with the same output in terms of frequency spectrum, the UWB system exhibits significantly lower spectral power density over more than 25% of its occupied bandwidth around the center frequency.
In contrast to conventional narrowband systems or wideband CDMA systems, this allows UWB to share frequency bands without causing interference, making it highly advantageous for coexistence with existing wireless communication systems.
The UWB (Ultra Wideband) system uses ultra-short pulses in the nanosecond or picosecond range, resulting in very low spectral power density across a very wide frequency range.
This enables high security, high data transmission rates, precise distance and position measurement, and strong resilience to multipath interference, all of which contribute to UWB's high-resolution performance.
Core Technologies of UWB
UWB (Ultra Wideband) is a type of communication technology capable of locating people or objects with high precision—typically within 10 to 30 centimeters. UWB communication commonly utilizes two core technologies: TDOA (Time Difference of Arrival) and TOF (Time of Flight).
TOF(Time of Flight)
TOF is a measurement method based on two-way ranging and response time.
In this method, a tag must send and receive signals multiple times with an anchor, and the distance between them is calculated based on the time it takes for the signal to travel.


TDoA(Time Difference of Arrival)
TDoA measures the time difference between when a signal arrives at multiple anchors.
This technique requires precise time synchronization among the anchors.
When using the TDoA method, a UWB tag sends a poll message, and all surrounding UWB anchors receive it and record the exact time of arrival.
By comparing these time differences, the system can accurately determine the location of the tag.


Comparison of TOF and TDoA
| Category | ToF | TDoA |
|---|---|---|
| Power consumption | High | Low |
| Tag capacity | Less | Less |
| Synchronization requirements | Low | High |
| Out of area positioning | Support | No Support |
Use Cases of UWB Technology
TOF(Time of Flight)
UWB enables highly accurate positioning even in indoor environments where GPS signals cannot reach.
It can be used to track the location of equipment and work zones in real time across a wide range of settings—including warehouses, logistics centers, sports facilities, industrial sites, airports, hospitals, ports, factories, and smart cities.
By doing so, UWB improves operational efficiency and enhances workplace safety.
Thanks to its high precision and low power consumption, UWB technology is being increasingly adopted in various industries.
UWB R&D in UWB Technology
SEUM Digital is a manufacturer and IT solutions provider specializing in the research and development of UWB module applications and a wide range of customized services.
We develop our own proprietary systems that encrypt precise location data to enable secure communication and ensure real-time location tracking and on-site situation control in any environment.
Our ongoing R&D focuses on integrated management solutions that enhance safety, responsiveness, and operational efficiency.

